
WordPress User Management
As the owner of your website, you may feel compelled to do everything yourself, including installing plugins, managing site settings, creating content, and moderating comments. However, this approach can quickly become overwhelming and is ultimately unsustainable.
Fortunately, WordPress has a feature known as User Roles, which enables you to create and assign users to specific roles in order to delegate your workload. As the Administrator, you’ll have full control over user management.
In this post, we’ll introduce you to WordPress user roles and management. This will include a breakdown of the different user roles, along with some plugins you can use to manage users and roles on your website. Let’s get started!
WordPress User Roles
To control what users have access to, WordPress uses a Roles system. There are six default WordPress user roles – Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, Subscriber, and Super Admin – and each has its own privileges and permissions.
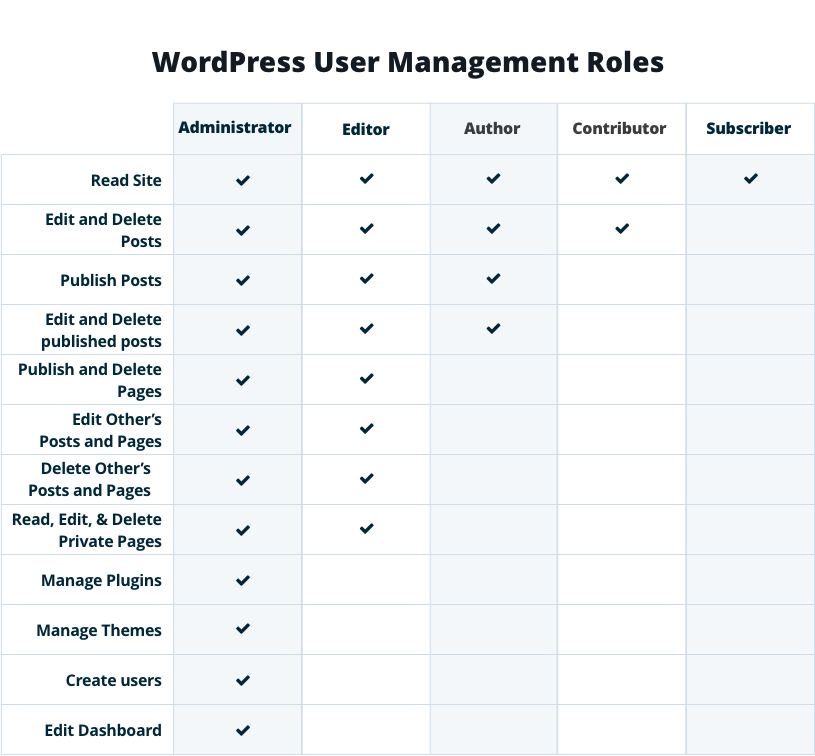
Administrator
Of all the WordPress roles, the Administrator role is the most powerful. Its permissions are not at all restricted.
A WordPress Admin can add new users, edit and delete current users, install new plugins and themes, make changes to the site’s settings, and much more. They also have full control over the website’s content. They can add new posts, edit both drafted and published posts, and even delete posts.
The Administrator role is often (though certainly not always) held by the site owner exclusively. This ensures that they have full control over the site, including how it runs and the content posted on it. However, that’s not to say that other user roles don’t have the ability to make certain restricted changes.
Editor
As the name implies, anyone with the Editor role has almost full control over the website’s page and post content. They can add, edit, publish, and delete posts on the website, including those added by other users (such as Authors and Contributors).
Another major permission the Editor role possesses is comments moderation. Any aspects of the site not related to content – including plugins, themes, and settings – cannot be affected by editors, nor any user levels below Editor (i.e. Author, Contributor, and Subscriber).
Author
Permissions held by the Author role relate to creating and publishing their own content. Authors can add, edit, publish, and delete their own posts (but not those of other contributors).
Unlike an Editor, this WordPress role is unable to moderate comments. However, an Author can still view comments.
Contributor
The WordPress Contributor role is popular on websites with user-submitted content (such as Lifehacker). While contributors can add and edit their own posts, they cannot publish them. They also cannot upload media files (unlike all of the roles already covered) or moderate comments.
Subscriber
The Subscriber role is the most restricted role available, and a Subscriber can only gain access to their User Profile—no other area of the back end is accessible. Subscribers can change their password, but that’s about it.
This role is most helpful if you want to require users to log in to read restricted content or leave comments.
Super Admin
The Super Admin role is a little different, as it’s specifically designed for use on WordPress multisite networks. As a Super Admin, you. can oversee and manage all of the sites in the same network.
This role is useful for network administrators, as well as designers who are assigned to multiple sites in the same network. It enables them to move freely among those sites, making necessary updates and changes.
WordPress User Role Management
We’ve outlined each of the user roles above and the permissions associated with each. However, it’s also important to clarify each role’s management privileges (if any).
The Administrator has full management capabilities. They can create and remove users at any time, and edit each specific role. An Administrator is the only default role that allows access to the list of user profiles active on the site, as well as any plugins (including WordPress user management plugins).
On a multisite network, the Super Admin has the same capabilities for all of the sites on the network. So the Super Admin can manage users on all of the network’s websites, while Administrators can manage users only on their specific site.
The other roles mentioned – Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber – have absolutely no user role management abilities. Users with each of these roles can view their own User Profile, but that’s the extent of it.
The management of a website’s users is an important task, and one not to be taken lightly. This is why the privilege is, by default, reserved for Administrators. However, the Administrator can extend user management capabilities to any user (or role) they want using one of the WordPress plugins mentioned below.
WordPress User Control
By taking charge of user control, Administrators can effectively manage user privileges and permissions. With the help of a user management WordPress plugin, Administrators can even create their own roles or customize permissions for each user. This makes the management of a WordPress website – and its various users – simpler.
WordPress User Management Plugins
While an Administrator has control over user roles in the WordPress back end, the default management and customization capabilities are limited. With plugins, you can expand these capabilities and more easily (and fully) manage the privileges and permissions of each role and user.
User Role Editor
The User Role Editor plugin is a popular option, with over 600,000 active downloads and a 4.5-star rating. This plugin puts control of all the various functions and permissions for WordPress user roles into an easy-to-navigate interface, which also works with multisite installations.
You can use checkboxes to toggle different permissions on or off for each of your user roles and save the new configurations to your website. This is a free plugin with extra modules available through a pro version that starts at $29 per year.
Members – Membership & User Role Editor Plugin
The Members plugin is designed to take user roles beyond the native WordPress functionality. With over 200,000 active downloads and a 4.5-star rating, it has a proven track record. The Members plugin also works seamlessly with MemberPress, which is useful if you’re running a membership website.
Some of this solution’s key features include the ability to restrict content from access by certain users, assign multiple roles to individual users, and edit what specific roles can do. Additionally, this plugin offers all of its core features in its free version.
WPFront User Role Editor
WPFront is a plugin that is growing in popularity and has a 4.5-star rating in the WordPress Plugin Directory. This tool uses an interface that will be familiar to WordPress users, as it mimics how you already manage posts and pages.
From the Role admin page, you’ll be able to add, edit, and delete roles, as well as migrate roles to other websites. While the free version of the plugin has plenty of features available, you can upgrade to the Pro version for enhanced options such as multisite support, content restrictions, and custom post type restrictions.
Remove Dashboard Access
The Remove Dashboard Access plugin is a useful option if you have many users on your website, and you want to secure your WordPress admin panel. With this plugin, you can control access to the dashboard by blocking specific user roles. Alternatively, you can allow certain users to access and edit just their user profiles.
This plugin also lets you create a custom login message for increased clarity, and designate a customized redirect URL for any disallowed users. This is a completely free plugin, with active development information available on GitHub.
PublishPress Capabilities: Manage WordPress Permissions and Edit User Roles
PublishPress Capabilities is a WordPress user management plugin with an intuitive, easy-to-use interface. With this plugin, you can easily create and delete user roles, as well as customize the permissions that each role or individual user has:
You can also create custom roles. For example, you could create a Master Author role that incorporates permissions from both the Editor and Author roles. Additionally, you can manage permissions for WooCommerce roles, and make copies and backups to restore or use on other websites.
Customize an Existing User Role
Using the Capabilities plugin from PublishPress is straightforward. Once you install and activate the plugin through your WordPress dashboard, you can access its settings by going to Capabilities in your main menu.
There, you can choose the existing role you want to edit in the top-right corner of the screen.
Then you can use the checkboxes to customize all of the capabilities for that role. If you have a WooCommerce shop, be sure to scroll all the way down to find the permissions for your online store as well. Once you have made your selections, click on Save Changes and you’re good to go.
Create a New Custom User Role
To create a new custom user role with the Capabilities plugin, you’ll need to first name your new role. Then select Create on the right-hand side of the settings page.
Once you do that, you’ll see that your new custom role is now selected in the Select Role to View/Edit field. You’ll also see confirmation that you create your new user role successfully.
Now you can configure the capabilities for your new role by using the checkboxes, and be sure to hit Save Changes when you’re done!
Other User Management Systems
Aside from plugins, there are also online services to help you fully manage your users and their permissions. They enable you to take a hands-on approach to user management, and many of these services are highly configurable.
For example, OAuth.io enables you to sign up, sign in, and otherwise manage your users’ sessions. With the oAuth.io API connected to your website, you can even update user data and keep track of when each user is logged in and active.
You might also want to check out Okta, an authentication system for websites and applications. Similar to oAuth.io, you can sign up and authenticate users. This gives you control over user security and ensures that your users (and website) are protected as well as possible.
Both of these options are great third-party solutions for a necessary and useful website management task.
Keep Learning with WP Engine
If simplicity is something that interests you, be sure to take a look at WP Engine’s managed hosting plans for WordPress. These plans ensure that your site is always up-to-task, and with 24/7 professional WordPress hosting support, you know that WP Engine has always got your back!
